Functional Medicine: A Passionate Practitioner's Guide
Functional medicine is a rapidly growing approach to healthcare that shifts the focus from treating symptoms to addressing the root causes of disease. Unlike conventional medicine, which often treats individual symptoms in isolation, functional medicine takes a holistic, systems-biology approach, considering the interconnectedness of the body's various systems. This guide will delve into the core principles, practical applications, and the passionate drive behind this innovative field.
What is Functional Medicine?
Functional medicine views the human body as an intricate network of interacting systems. Instead of simply suppressing symptoms with medication, functional medicine practitioners seek to identify and correct the underlying imbalances contributing to illness. This involves a thorough investigation into a patient's lifestyle, genetics, environment, and overall well-being to create a personalized treatment plan. The goal isn't just to manage a disease but to restore optimal health and prevent future problems.
Core Principles of Functional Medicine
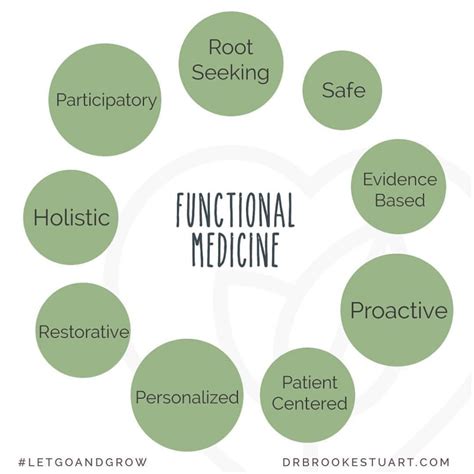
Several key principles underpin the functional medicine approach:
- Patient-centered care: The patient is actively involved in the diagnostic and treatment process, fostering a collaborative relationship between practitioner and patient.
- Holistic approach: The practitioner considers the whole person, including physical, mental, and emotional factors, rather than focusing on isolated symptoms.
- Systems biology: Understanding how different body systems interact and influence one another is crucial for identifying root causes.
- Addressing root causes: The primary aim is to identify and address the underlying imbalances that contribute to disease, rather than simply managing symptoms.
- Lifestyle interventions: Dietary changes, exercise, stress management, and sleep optimization are often central to treatment plans.
- Personalized treatment: Plans are tailored to the individual patient's unique needs and circumstances.
How Does Functional Medicine Differ from Conventional Medicine?
The key difference lies in the approach to diagnosis and treatment. Conventional medicine often relies on diagnostic tests and prescribed medications to address specific symptoms. Functional medicine, while utilizing conventional diagnostic tools, delves deeper, investigating the patient's history, lifestyle, and environmental factors to uncover the root causes of illness. It emphasizes prevention and empowers individuals to take control of their health.
H2: What are the benefits of Functional Medicine?
Functional medicine offers several potential benefits:
- Improved overall well-being: By addressing root causes, it can lead to significant improvements in overall health and vitality.
- Chronic disease prevention: By identifying and correcting underlying imbalances, it can help prevent the development of chronic diseases.
- Personalized treatment plans: Tailored approaches cater to individual needs, increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
- Empowerment: It empowers patients to actively participate in their healthcare, taking responsibility for their well-being.
- Improved quality of life: By addressing the root causes of health problems, functional medicine can improve overall quality of life.
H2: What conditions can Functional Medicine treat?
Functional medicine isn't a cure-all, but it can be a valuable approach for a wide range of conditions, including:
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus.
- Digestive disorders: Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn's disease, and celiac disease.
- Chronic fatigue syndrome: Persistent and debilitating fatigue.
- Hormonal imbalances: Conditions affecting thyroid function, adrenal function, and reproductive health.
- Neurological conditions: Certain neurological conditions such as fibromyalgia and migraines.
H2: How do I find a Functional Medicine practitioner?
Finding a qualified practitioner is crucial. Look for practitioners certified by the Institute for Functional Medicine (IFM) or other reputable organizations. You can also search online directories or ask for recommendations from your primary care physician or other healthcare professionals.
H2: What tests are typically used in Functional Medicine?
Functional medicine utilizes a range of tests to assess various aspects of a patient's health. These can include:
- Blood tests: Comprehensive metabolic panels, hormone tests, nutrient level assessments.
- Stool tests: Gut microbiome analysis, assessment of digestive function.
- Urine tests: Assessment of detoxification pathways, hormone levels.
- Genetic testing: Identification of genetic predispositions to certain conditions.
H2: Is Functional Medicine covered by insurance?
Insurance coverage for functional medicine varies widely depending on the specific tests and treatments involved and the individual insurance plan. It's crucial to check with your insurance provider before undergoing any functional medicine treatments.
H2: What is the future of Functional Medicine?
As scientific understanding of the body's intricate systems continues to advance, functional medicine is poised for even greater growth and acceptance. The increasing focus on personalized medicine and prevention aligns perfectly with the core principles of functional medicine, suggesting a bright future for this holistic healthcare approach.
This guide provides a general overview of functional medicine. It's not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions related to your health.