Drain Field Location: Everything You Need to Know
Choosing the right location for your drain field is crucial for a properly functioning septic system. A poorly placed drain field can lead to costly repairs, environmental damage, and unpleasant odors. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about selecting the optimal location for your drain field, ensuring years of trouble-free operation.
What is a Drain Field?
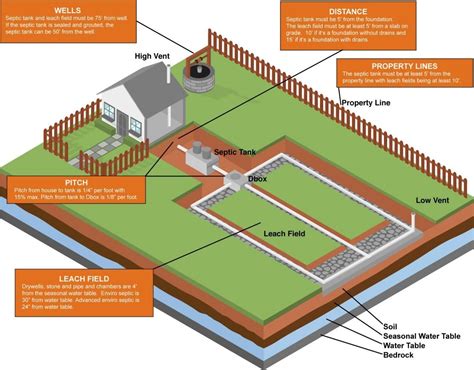
Before diving into location specifics, let's clarify what a drain field is. A drain field, also known as a leach field or absorption field, is a component of your septic system responsible for treating wastewater. It consists of perforated pipes surrounded by gravel or other porous material, allowing treated wastewater to slowly seep into the surrounding soil. The soil then naturally filters the wastewater, removing contaminants before it reaches groundwater. The effectiveness of this process depends heavily on the drain field's location.
Factors Affecting Drain Field Location
Several critical factors influence the ideal placement of your drain field. Ignoring these can lead to system failure and environmental contamination.
1. Soil Type and Permeability
The soil's ability to absorb and filter wastewater is paramount. Sandy loam soils are generally ideal, offering excellent drainage. Clay soils, on the other hand, retain water and are unsuitable for drain fields. A professional soil percolation test (perc test) is essential to determine your soil's suitability. This test measures the rate at which water percolates through the soil.
2. Groundwater Level
The drain field must be located above the water table to prevent wastewater from backing up into the system. A high water table limits the available space for wastewater absorption. Your local health department or a licensed septic installer can help determine the groundwater level on your property.
3. Distance from Buildings and Water Sources
The drain field should be a safe distance from your house, well, and other water sources to prevent contamination. Specific distances vary by local regulations but generally require a minimum separation. Always consult your local building codes for exact requirements.
4. Topography and Slope
The land's slope significantly impacts drain field design. A gentle slope is preferable, allowing for proper drainage and preventing wastewater from pooling. Steep slopes can require more complex and costly installation techniques.
5. Vegetation and Trees
Trees and large shrubs with extensive root systems should be avoided near the drain field. Roots can penetrate the pipes and gravel, causing blockages and system failure. Keep the area around the drain field clear of vegetation to facilitate maintenance and inspection.
Frequently Asked Questions (PAAs)
Here are some common questions regarding drain field location, addressed to provide comprehensive understanding:
How far from the house should a drain field be?
The minimum distance between a drain field and your house is determined by local regulations, typically ranging from 10 to 50 feet. This distance is crucial to prevent wastewater from contaminating your home's foundation. Always consult your local building codes for precise requirements.
What is a perc test, and why is it important?
A percolation test (perc test) assesses the soil's ability to absorb water. It's crucial for determining the suitability of a site for a drain field. The test involves digging holes and measuring the rate at which water drains into the soil. The results guide the design of the drain field to ensure proper wastewater absorption.
Can I install a drain field myself?
While it may seem like a DIY project, installing a drain field is complex and requires specialized knowledge and equipment. Improper installation can lead to system failure and environmental contamination. It’s highly recommended to hire a licensed septic installer to ensure the work meets all regulations and standards.
What happens if my drain field is improperly located?
An improperly located drain field can result in several problems: system failure, wastewater backup, contamination of groundwater and nearby water sources, and unpleasant odors. These issues can be expensive to rectify and may require extensive repairs or even complete system replacement.
How often should I have my drain field inspected?
Regular inspection of your septic system, including the drain field, is crucial for preventing problems. The frequency of inspection depends on several factors, but a yearly inspection is generally recommended. A licensed professional can detect potential issues early, preventing costly repairs.
Conclusion
Selecting the proper location for your drain field is a critical step in ensuring the long-term functionality and efficiency of your septic system. By carefully considering soil type, groundwater level, distances from structures and water sources, topography, and vegetation, you can avoid costly mistakes and environmental hazards. Remember to always consult with local authorities and a licensed septic installer to ensure compliance with regulations and optimal system performance. Ignoring these factors could lead to significant problems down the line.