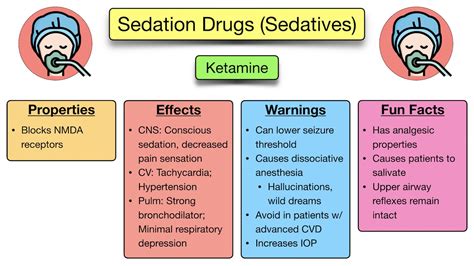
Understanding Sedation: Duration & Side Effects
Sedation, the state of being calmed or tranquilized, is frequently used in medical procedures and dentistry. Understanding its duration and potential side effects is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals. This article delves into the intricacies of sedation, exploring its various types, typical durations, and potential side effects, empowering you with knowledge to make informed decisions.
What is Sedation?
Sedation is a medically induced state of reduced awareness, ranging from mild relaxation to unconsciousness. The level of sedation administered depends entirely on the procedure and the patient's individual needs. It's important to note that sedation is different from general anesthesia, though they share some similarities. General anesthesia involves a complete loss of consciousness, while sedation allows for varying degrees of responsiveness.
Types of Sedation
Several types of sedation exist, each with a different level of consciousness and responsiveness:
-
Minimal Sedation (Anxiolysis): The patient remains conscious and can respond to verbal commands. This level is often used for minor procedures or to alleviate anxiety.
-
Moderate Sedation (Conscious Sedation): The patient is relaxed and may be drowsy but can still respond to verbal commands and physical stimulation. This is commonly used for dental procedures and some minor surgeries.
-
Deep Sedation: The patient is unresponsive to verbal commands but may respond to painful stimuli. This level requires close monitoring by medical professionals.
-
General Anesthesia: The patient is completely unconscious and unable to respond to any stimuli. This is typically used for major surgeries.
How Long Does Sedation Last?
The duration of sedation varies widely depending on the type of sedative used, the dose administered, and the patient's individual metabolism. There's no single answer to "how long does sedation last?". However, here's a general guideline:
-
Minimal Sedation: Effects typically wear off within a short time, often less than an hour.
-
Moderate Sedation: The effects usually last for a few hours, but recovery time can vary.
-
Deep Sedation: Recovery from deep sedation can take several hours, and close monitoring is essential during this period.
Important Note: Always follow your doctor or dentist's post-procedure instructions. Do not drive or operate machinery until fully recovered.
Common Side Effects of Sedation
While sedation is generally safe, it can produce several side effects, ranging from mild to severe. The likelihood and severity of side effects depend on the type and dose of sedative used, as well as individual patient factors like age and pre-existing health conditions.
Mild Side Effects
These are common and usually resolve on their own:
-
Drowsiness: This is a common side effect, particularly after moderate or deep sedation.
-
Nausea: Some patients experience nausea, sometimes accompanied by vomiting.
-
Dry Mouth: This can be uncomfortable but usually resolves quickly.
-
Headache: Mild headaches are possible following sedation.
-
Dizziness: This can be a temporary side effect.
More Serious Side Effects (Less Common but Require Immediate Medical Attention)
-
Respiratory Depression: This is a serious complication that involves slowed or shallow breathing. It requires immediate medical attention.
-
Hypotension (Low Blood Pressure): A significant drop in blood pressure can be dangerous.
-
Cardiac Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats can occur.
-
Allergic Reactions: Allergic reactions to sedatives, although rare, can be severe and life-threatening.
What are the Risks of Sedation?
The risks associated with sedation are generally low when administered by qualified medical professionals in a controlled environment. However, potential risks include respiratory depression, allergic reactions, and complications related to pre-existing medical conditions. A thorough medical history and pre-operative assessment are crucial to minimize these risks.
Can I Drive After Sedation?
No. Never drive or operate machinery after receiving sedation, even if you feel alert. Sedatives can impair judgment, coordination, and reaction time for several hours after the procedure. Always arrange for someone to drive you home and provide supervision during the recovery period.
How to Minimize Sedation Side Effects
Following your doctor's or dentist's instructions carefully is paramount. This includes adhering to pre-procedure guidelines (like fasting) and post-procedure recommendations (like avoiding alcohol or certain medications). Open communication with your healthcare provider about any concerns or pre-existing conditions will help minimize risks and ensure a safe and comfortable experience.
This information is for general knowledge and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.