The Impact of Metals on Our Environment: A Comprehensive Overview
Metals are integral to modern life, underpinning our infrastructure, technology, and countless everyday objects. However, the extraction, processing, and disposal of these vital materials carry significant environmental consequences. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing sustainable practices and mitigating the risks to our planet. This article explores the multifaceted effects of metals on the environment, addressing key concerns and potential solutions.
What are the main environmental impacts of metal mining?
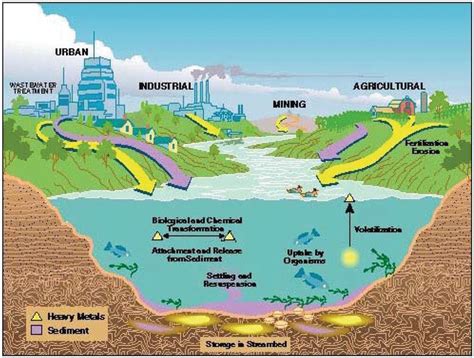
Metal mining's environmental footprint is substantial. The process often involves deforestation, habitat destruction, and soil erosion. Large-scale excavations alter landscapes dramatically, impacting biodiversity and ecosystem services. Further, mining activities generate vast amounts of waste rock and tailings, which can contain toxic heavy metals like arsenic, lead, and mercury. These materials can leach into water sources, contaminating rivers, lakes, and groundwater, posing significant risks to human and aquatic life. Acid mine drainage, a particularly severe consequence, occurs when sulfide minerals in exposed rock react with water and air, producing highly acidic runoff laden with dissolved metals.
How do metals affect water quality?
Water pollution from metal mining and industrial processes is a major environmental concern. Heavy metals are non-biodegradable and persist in the environment, accumulating in the food chain through bioaccumulation. This process concentrates toxins at higher trophic levels, posing risks to top predators, including humans. Even at low concentrations, some metals like mercury can cause severe neurological damage. Water contaminated with metals can also impact aquatic ecosystems, harming fish populations and disrupting delicate aquatic food webs.
What are the effects of metal pollution on soil?
Metal contamination of soil affects plant growth and overall soil health. High concentrations of heavy metals can inhibit nutrient uptake by plants, leading to stunted growth and reduced yields. This impacts agriculture and food security. Furthermore, contaminated soil can restrict the growth of beneficial microorganisms, vital for maintaining soil fertility and structure. The mobility and bioavailability of metals in soil vary depending on factors like pH, soil type, and the presence of organic matter. These complex interactions determine the extent of their impact on the surrounding environment.
What are the health risks associated with metal exposure?
Human exposure to metals can occur through various pathways, including contaminated water, food, and air. The health impacts are diverse and depend on the specific metal, exposure level, and duration. Some metals, like lead, are neurotoxic, particularly harmful to children's developing brains. Others, such as cadmium and arsenic, are carcinogenic, increasing the risk of cancer. Chronic exposure to even low levels of heavy metals can lead to various health problems, including kidney damage, respiratory issues, and reproductive disorders.
How can we reduce the environmental impact of metals?
Mitigating the environmental impact of metals requires a multi-pronged approach:
- Sustainable Mining Practices: Implementing responsible mining practices, including minimizing waste generation, effective tailings management, and water treatment, is crucial. This also includes exploring less environmentally damaging extraction techniques.
- Recycling and Reuse: Recycling metals significantly reduces the need for new mining operations. Improving recycling infrastructure and promoting the reuse of metal products are vital steps.
- Technological Advancements: Research and development of cleaner metal production technologies, such as using less energy and generating fewer harmful byproducts, are crucial for reducing environmental burdens.
- Stricter Regulations: Robust environmental regulations and enforcement are essential to ensure that mining and industrial activities adhere to environmental standards.
- Public Awareness: Raising public awareness about the environmental impacts of metals and promoting responsible consumption patterns are vital for driving positive change.
What is the future of metal production and environmental sustainability?
The future of metal production hinges on achieving a balance between meeting societal demands and protecting the environment. This necessitates a paradigm shift towards a circular economy model, emphasizing resource efficiency, waste reduction, and responsible materials management. Investment in research and development of sustainable technologies and practices is critical for creating a more sustainable future. Collaboration between governments, industries, and researchers is essential for developing and implementing effective strategies to mitigate the environmental impacts of metals and ensure a healthier planet for future generations.