The Essential Guide to Chinese Furniture Joinery and Dating
Chinese furniture, renowned for its elegance, durability, and intricate craftsmanship, stands as a testament to centuries of refined woodworking techniques. Understanding its joinery methods is key to appreciating its artistry and assessing its age and authenticity. This guide delves into the essential aspects of Chinese furniture joinery and the methods used for dating these exquisite pieces.
What are the Key Joinery Techniques Used in Chinese Furniture?
The beauty of Chinese furniture lies not just in its design but in the invisible strength of its joinery. Unlike Western furniture that often relies heavily on glue and nails, traditional Chinese furniture emphasizes intricate interlocking joints, showcasing the skill and artistry of the craftsman. Several key techniques stand out:
-
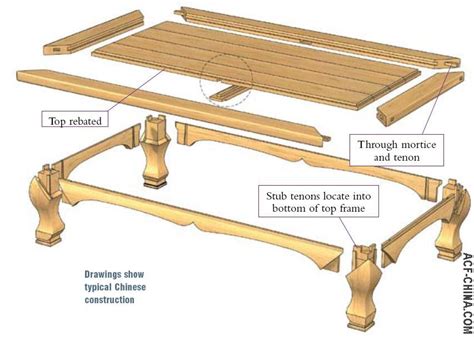
Mortise and Tenon (榫卯, sǔn mǎo): This is the cornerstone of Chinese furniture joinery. A tenon (a projecting peg) is precisely carved to fit snugly into a mortise (a corresponding hole). Variations abound, each named for its unique shape and function: through tenons, half-laps, blind tenons, etc. The strength and precision of these joints are remarkable, requiring minimal or no glue.
-
Dovetail Joints (燕尾榫, yàn wěi sǔn): While less common than mortise and tenon, dovetail joints add a distinct aesthetic element, particularly in drawer construction. These interlocking tapered pins create a strong and visually appealing bond.
-
Shoulder Tenons (企口榫, qǐ kǒu sǔn): This type of tenon has a shoulder that rests against the surface of the mortise, adding extra stability and preventing movement. They are frequently used in leg-and-rail constructions.
-
Through Tenons with Wooden Pins (明榫, míng sǔn): These are visible tenons, often reinforced with wooden pins for added strength. While functional, they also contribute to the aesthetic appeal of the piece.
How is Wood Used and Identified in Chinese Furniture?
The type of wood used is crucial for both dating and assessing the quality of a piece. Common woods include:
-
Hardwoods: Rosewood (various types), Huanghuali (a highly prized and expensive hardwood), and teak were frequently employed for their durability and rich colors.
-
Softwoods: While less common in fine furniture, softwoods like pine were sometimes used for less visible parts.
Identifying the specific wood requires expertise, often involving microscopic analysis. The wood's color, grain, and scent can provide clues, but careful examination is essential.
Dating Chinese Furniture: What Clues Should You Look For?
Dating antique Chinese furniture is a complex endeavor, requiring a deep understanding of historical styles, woodworking techniques, and materials. Several factors can help pinpoint a piece's age:
-
Style: Different dynasties and periods favored specific design elements, proportions, and decorative motifs. Studying the evolution of these styles is crucial for accurate dating.
-
Wood Type and Quality: The type of wood and its condition can offer insights. Certain woods were more prevalent during specific periods.
-
Joinery Techniques: The sophistication and complexity of the joinery can indicate the age of the piece. Earlier pieces might exhibit simpler joinery than later ones.
-
Hardware: The type and style of hardware (hinges, locks, etc.) can provide important clues. Changes in metalworking techniques throughout history leave characteristic marks.
-
Finish: The type of finish and its wear can reveal information about the piece's age.
How can I Tell if My Chinese Furniture is Antique or a Reproduction?
Distinguishing between antique and reproduction Chinese furniture requires careful observation and expert knowledge. Reproductions often lack the subtle nuances of age and craftsmanship found in authentic antiques:
-
Examine the joinery closely: Look for inconsistencies, machine-made marks, or the use of glue where traditional techniques would have sufficed.
-
Check the wood for signs of age: Look for patina, natural wear, and the characteristic aging of the wood. Reproductions often try to simulate aging artificially, but usually fall short.
-
Inspect the finish: A genuine antique will usually have a finish that has aged naturally over time, exhibiting subtle variations and imperfections.
-
Seek expert advice: Consulting with an experienced appraiser or antique furniture specialist is always recommended.
What are some common characteristics of antique Chinese furniture?
Antique Chinese furniture often displays:
-
Subtle Patina: A rich, aged look developed over time.
-
Intricate Hand-Carved Details: Often featuring detailed carvings not easily replicated by machine.
-
Consistent Ageing: Wear and tear will be consistent with the overall age of the piece.
-
Authentic Hardware: Hardware will be consistent with the time period.
How can I learn more about Chinese furniture dating and joinery?
Further research can be undertaken through:
-
Books and scholarly articles: Numerous resources explore the history and techniques of Chinese furniture making.
-
Museums and exhibitions: Visiting museums with collections of Chinese furniture is invaluable for firsthand observation.
-
Expert consultation: Seeking guidance from furniture appraisers or specialists provides deeper insight.
This guide provides a foundational understanding of Chinese furniture joinery and dating. Remember, accurate assessment often requires expertise and careful examination. The rich history and sophisticated craftsmanship embedded in these pieces make them both functional works of art and fascinating historical artifacts.