Negotiating Royalties: Protecting Your Song Rights
Securing fair royalties for your songwriting is crucial. It's the lifeblood of your career, ensuring you're compensated for the creative work that fuels your musical endeavors. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the often-complex world of royalty negotiations, helping you protect your song rights and maximize your earnings. Understanding the different types of royalties, common negotiation tactics, and how to build strong relationships with publishers and other stakeholders is key to success.
What are Music Royalties?
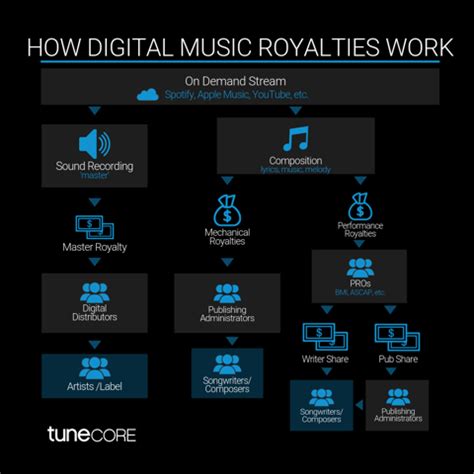
Music royalties are payments made to songwriters and composers for the use of their copyrighted musical works. These payments are triggered whenever your song is performed, reproduced, or distributed in various ways. They're not just about record sales; they encompass a far broader spectrum of usage.
Types of Royalties: Understanding the Landscape
Several types of royalties exist, each associated with a specific form of your song's use. Knowing the difference is paramount in ensuring you receive the compensation you deserve.
Mechanical Royalties:
These are paid to songwriters whenever their songs are reproduced or distributed in physical formats (CDs, vinyl) or digital formats (downloads, streams). The rate is legally mandated in many countries, offering a baseline level of protection.
Performance Royalties:
Collected through organizations like ASCAP, BMI, and SESAC, these royalties are generated when your songs are performed publicly – in concerts, on radio, television, or online streaming services. The amount depends on the frequency and location of the performance.
Synchronization Royalties (Sync):
When your song is used in a visual medium like a film, television show, commercial, or video game, you're entitled to synchronization royalties. These fees often command higher rates due to the significant exposure and potential for increased song recognition.
Print Royalties:
These are paid when your sheet music is sold or distributed.
How to Negotiate Royalties Effectively
Negotiating royalties requires preparation, confidence, and a clear understanding of your song's value and market position. Here's a strategic approach:
1. Know Your Worth: Market Research is Key
Before entering any negotiation, thoroughly research industry standards for similar artists and song types. Analyze royalty rates offered in comparable deals to establish a realistic benchmark.
2. Choose Your Representatives Wisely:
A skilled music lawyer or experienced music business manager can provide invaluable guidance throughout the process. They will protect your interests and ensure the contract is fair and protects your rights.
3. Understand the Contract Inside and Out:
Don't sign anything you don't fully understand. Take your time, seek professional legal advice, and thoroughly review every clause. Pay particular attention to the duration of the agreement, termination clauses, and royalty payment structures.
4. Be Prepared to Walk Away:
If the deal doesn't meet your expectations or adequately protect your rights, be prepared to walk away. Your creative work is valuable, and you shouldn't compromise your interests for a less-than-ideal agreement.
5. Build Strong Relationships:
Cultivating positive relationships with publishers, record labels, and other stakeholders is crucial for long-term success. Mutual respect and trust can lead to more favorable negotiation outcomes in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (PAAs)
Here are some common questions surrounding royalty negotiations:
How much are music royalties typically?
The amount of music royalties varies greatly depending on several factors, including the type of royalty (mechanical, performance, sync), the usage of the song, the artist’s popularity and the specific contract negotiated. There's no single answer, and a skilled negotiator will ensure you secure the highest possible rate within the market context.
What are the common royalty rates for streaming services?
Royalty rates for streaming services are typically much lower than traditional sales models. The rates vary widely across different streaming platforms and also depend on the type of licensing agreement and how the song is used. The rates are often expressed as a percentage of revenue earned from subscriptions.
How do I collect my royalties?
You typically collect royalties through Performing Rights Organizations (PROs) like ASCAP, BMI, and SESAC for performance royalties, and through your publisher, record label, or directly from licensees for mechanical and synchronization royalties. Regular monitoring of your royalty statements is essential to ensure accurate payments.
Can I negotiate royalty rates after signing a contract?
Negotiating royalty rates after signing a contract is generally difficult, but not impossible. This usually requires demonstrating exceptional success or substantial changes in the market that significantly impact your value. This is where having a strong legal team is paramount.
What should I do if I believe I'm not receiving the correct royalties?
If you suspect inaccuracies in your royalty statements, carefully review your contract and the relevant accounting information. Contact your publisher or relevant parties and request a detailed explanation of any discrepancies. If this doesn’t resolve the issue, you might need to consult with a lawyer.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Creative Investment
Negotiating royalties isn't just about securing income; it's about protecting your creative legacy and ensuring that your hard work translates into fair financial compensation. By understanding the different types of royalties, employing effective negotiation strategies, and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can safeguard your rights and build a sustainable career in the music industry. Remember, your music is valuable, and you deserve to be fairly compensated for it.