Mexico: A Geographic Overview and Size Comparison
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a vibrant North American nation boasting a rich tapestry of cultures, history, and geography. Its diverse landscape, stretching from arid deserts to lush rainforests, makes it a fascinating subject for geographic exploration. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of Mexico's geography and delve into comparisons with other countries to better understand its size and scale.
What is the geographical location of Mexico?
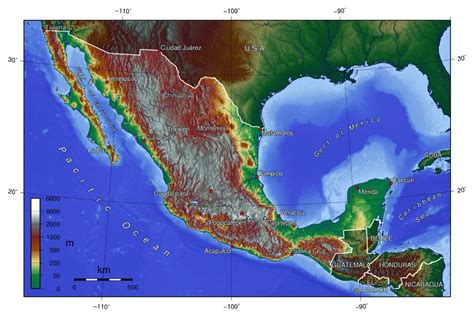
Mexico occupies a unique geographical position, bridging the North American continent and linking it to Central America. It's bordered to the north by the United States, to the south by Guatemala and Belize, and to the west by the Pacific Ocean and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea. This strategic location has profoundly shaped its history, culture, and economy.
What are the major geographical features of Mexico?
Mexico's geography is incredibly diverse, showcasing a range of dramatic landscapes. Key features include:
-
The Sierra Madre Mountains: This extensive mountain range runs along the western and eastern coasts, creating significant topographical variation. The Sierra Madre Occidental and Sierra Madre Oriental are its principal ranges.
-
The Mexican Plateau: A vast, high-altitude plateau situated between the Sierra Madre ranges, it forms the heartland of Mexico, home to many major cities and significant agricultural areas.
-
The Yucatán Peninsula: A low-lying, limestone peninsula in southeastern Mexico, known for its distinctive karst topography, cenotes (sinkholes), and Mayan ruins.
-
The Baja California Peninsula: A long, narrow peninsula extending south from California, characterized by deserts, mountains, and coastal regions.
-
Coastal Plains: Narrow coastal plains fringe both the Pacific and Atlantic coasts, offering fertile land for agriculture and supporting a significant population.
How big is Mexico compared to other countries?
Understanding Mexico's size requires comparing it to other well-known nations:
-
Mexico vs. the United States: Mexico is considerably smaller than the United States, approximately one-third the size.
-
Mexico vs. Canada: Similar to its relationship with the US, Mexico is significantly smaller than Canada.
-
Mexico vs. Western European Countries: Mexico is larger than most Western European countries, comparable in size to nations like Spain, France, or Germany. However, it's important to note that population density differs significantly.
-
Mexico vs. other Latin American Countries: Within Latin America, Mexico ranks amongst the larger countries, smaller than Brazil or Argentina, but larger than many others.
How does Mexico's area compare to the states of the US?
To further illustrate its size, consider this: Mexico's area is roughly comparable to the combined area of several large US states. For example, it's slightly larger than Alaska alone, but significantly smaller than the combined area of Alaska and Texas.
What are the major climate zones in Mexico?
Mexico's diverse geography results in a range of climate zones:
-
Arid and Semi-arid: Much of the northern and central plateau experiences arid and semi-arid conditions, characterized by low rainfall and high temperatures.
-
Tropical: The southern regions, particularly along the coasts, have a tropical climate with high humidity and abundant rainfall.
-
Temperate: Higher altitudes in the mountains experience temperate climates, with cooler temperatures and varying rainfall patterns.
What are the major ecosystems in Mexico?
Mexico is home to a wide array of ecosystems, showcasing remarkable biodiversity:
-
Deserts: Sonoran, Chihuahuan, and other desert ecosystems thrive in the drier regions.
-
Rainforests: Lush rainforests are found in the southern and southeastern parts of the country.
-
Forests: Diverse forest ecosystems, including pine-oak forests, are widespread throughout the mountains.
-
Coastal Ecosystems: Mangroves, beaches, and coral reefs form vital coastal ecosystems.
How does Mexico's geography impact its economy?
Mexico's geography significantly impacts its economy. The fertile lands support agriculture, while its diverse resources, including minerals, oil, and timber, contribute to its industrial sector. Its coastal regions facilitate international trade and tourism, a major part of its economy.
This comprehensive overview offers a deeper understanding of Mexico's diverse geography and its relative size compared to other countries. Its unique location, varied landscapes, and rich biodiversity make it a geographically fascinating and economically significant nation.