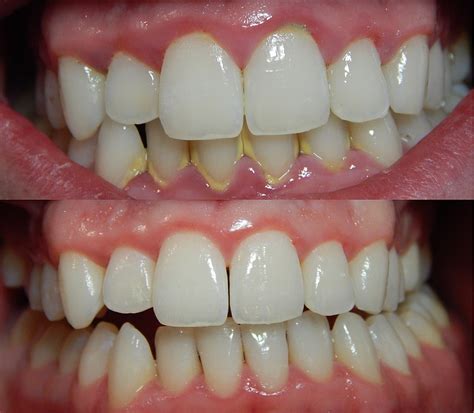
Gingivitis: Shorten Your Healing Time Now
Gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease, is characterized by inflamed gums that are often red, swollen, and bleed easily. While it's a common condition, it's crucial to address it promptly to prevent it from progressing to periodontitis, a more serious form of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss. This article explores effective ways to shorten your gingivitis healing time and restore your oral health.
What Causes Gingivitis?
The primary culprit behind gingivitis is plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that constantly forms on your teeth. If not removed through regular brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar (calculus), providing a breeding ground for harmful bacteria. These bacteria produce toxins that irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and gingivitis. Other contributing factors include:
- Poor oral hygiene: Insufficient brushing and flossing are major culprits.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can increase susceptibility to gingivitis.
- Smoking: Smoking reduces blood flow to the gums, hindering their ability to heal and making them more vulnerable to infection.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as those that cause dry mouth, can increase the risk of gingivitis.
- Genetics: A family history of gum disease can increase your risk.
- Systemic diseases: Conditions like diabetes can worsen gum disease.
How Long Does Gingivitis Take to Heal?
The healing time for gingivitis varies depending on the severity of the inflammation and the individual's response to treatment. With consistent and proper oral hygiene, gingivitis can often improve within a few weeks. However, neglecting treatment can lead to chronic gingivitis or progression to periodontitis.
How to Shorten Gingivitis Healing Time
Effective treatment focuses on eliminating plaque and bacteria and promoting gum tissue healing. Here's how to accelerate the process:
1. Improve Your Oral Hygiene Routine
- Brush twice daily: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, paying attention to the gum line. Consider an electric toothbrush for more effective plaque removal.
- Floss daily: Flossing removes plaque and food particles from between teeth where your toothbrush can't reach.
- Use an antimicrobial mouthwash: This can help kill bacteria and reduce inflammation. Choose a mouthwash recommended by your dentist.
2. Professional Dental Cleaning
Regular professional cleanings are essential. A dental hygienist can remove hardened tartar and plaque that you can't remove at home, significantly reducing bacterial load and promoting healing.
3. Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall health, including gum health. Foods rich in vitamin C, antioxidants, and calcium are particularly beneficial.
4. Quit Smoking
Smoking significantly impairs gum healing. Quitting smoking is crucial for effective gingivitis treatment and preventing further complications.
5. Manage Underlying Medical Conditions
If you have diabetes or other systemic diseases, managing these conditions effectively is vital for improving gum health. Work closely with your physician and dentist.
What if Gingivitis Doesn't Improve?
If you've implemented these strategies and your gingivitis persists or worsens, it's crucial to consult your dentist immediately. Persistent gingivitis may indicate periodontitis, requiring more advanced treatment. Your dentist can diagnose the problem and recommend appropriate treatment options, such as scaling and root planing (deep cleaning) or antibiotic therapy.
Can Gingivitis Be Prevented?
Yes! The best way to shorten gingivitis healing time is to prevent it altogether. Maintaining excellent oral hygiene, regular dental checkups and cleanings, and addressing any underlying health conditions are key preventative measures.
Frequently Asked Questions (PAA)
Q: Is gingivitis contagious?
A: Gingivitis itself isn't contagious, but the bacteria that cause it can be transmitted through saliva sharing (e.g., sharing utensils or kissing).
Q: Can gingivitis cause bad breath?
A: Yes, the bacteria associated with gingivitis produce volatile sulfur compounds, leading to bad breath (halitosis).
Q: Does gingivitis always lead to periodontitis?
A: No, with prompt and effective treatment, gingivitis can often be reversed before it progresses to periodontitis. However, neglecting treatment significantly increases the risk of progression.
Q: What are the long-term effects of untreated gingivitis?
A: Untreated gingivitis can lead to periodontitis, which can cause tooth loss, bone loss, and even impact overall health.
Q: How can I tell the difference between gingivitis and periodontitis?
A: Gingivitis primarily involves gum inflammation and bleeding. Periodontitis involves deeper gum pockets, bone loss, and potentially loose teeth. Only a dentist can accurately diagnose the condition.
By actively addressing gingivitis with improved oral hygiene, professional care, and lifestyle modifications, you can significantly shorten your healing time and protect your long-term oral health. Remember, early intervention is key to preventing more serious complications.