Conduit Depth: Easy Steps for Accurate Installation
Proper conduit depth is crucial for electrical safety and code compliance. Burying conduit too shallowly exposes it to damage, while burying it too deeply makes installation and future maintenance unnecessarily difficult and expensive. This comprehensive guide outlines the easy steps for accurate conduit installation, ensuring a safe and efficient electrical system. We'll cover everything from determining the appropriate depth to addressing common challenges and utilizing helpful tools.
What Determines Conduit Depth?
Several factors influence the required depth of your conduit installation. These include:
-
Local Codes: This is the most important factor. Your local building codes will specify minimum burial depths for conduits, often varying based on the type of conduit (PVC, metal, etc.) and the location (residential, commercial, industrial). Always consult your local authority having jurisdiction (AHJ) for precise requirements. Ignoring local codes can result in significant penalties.
-
Soil Conditions: Rocky or hard-packed soil may require more effort to dig and may necessitate a shallower depth compared to loose, easily excavated soil. The type of soil will also affect the conduit's protection from damage.
-
Traffic Conditions: Areas with high pedestrian or vehicular traffic necessitate deeper burial depths to protect the conduit from damage.
-
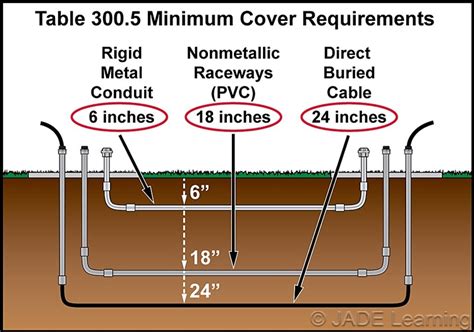
Type of Conduit: Different conduit types (e.g., PVC, rigid metal conduit (RMC), flexible metal conduit (FMC)) may have different minimum burial depth requirements outlined in the relevant codes.
-
Freezing Depth: In colder climates, conduits carrying electrical wiring need to be buried below the local frost line to prevent water freezing within the conduit and causing damage. This depth varies significantly by geographic location.
How to Determine the Correct Conduit Depth
-
Consult Local Codes: The first and most important step is to contact your local building department or AHJ. Obtain a copy of the relevant electrical codes for your area. These codes will provide the minimum allowable burial depth for conduits under various conditions.
-
Check for Existing Utilities: Before digging, always call your local utility companies to locate and mark underground utilities such as gas lines, water pipes, and other cables. This crucial safety step prevents accidental damage and potential hazards.
-
Determine Frost Line Depth: If you live in a climate with freezing temperatures, determine the local frost line depth. This information is usually available from your local building department or through online resources specific to your region. Your conduit must be buried below this depth.
-
Consider Soil Conditions: Assess the soil type on your property. Rocky or hard soil may require additional considerations for excavation and conduit placement.
-
Plan for Future Access: While burying the conduit deep enough for protection is important, leave enough space to easily access the conduit for repairs or future additions.
What Happens If Conduit is Too Shallow?
Burying conduit too shallowly presents several significant risks:
-
Damage: The conduit is more vulnerable to damage from landscaping, digging, or other ground disturbances.
-
Exposure to the Elements: Shallow conduits are more susceptible to moisture and corrosion, leading to potential electrical hazards.
-
Code Violations: Failing to meet minimum burial depth requirements will result in code violations and potential penalties.
-
Safety Risks: Damaged or exposed conduits increase the risk of electric shock, short circuits, and potential fires.
How to Install Conduit at the Correct Depth
-
Excavation: Dig a trench of the required depth and width. The trench should be wide enough to comfortably accommodate the conduit and any backfill material.
-
Backfill Material: Use compacted backfill material around the conduit to prevent shifting and damage. Avoid using rocks or materials that could puncture the conduit.
-
Marking the Location: Clearly mark the location of the conduit above ground to avoid accidental damage during future excavation or landscaping.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the typical conduit depth for residential applications?
Typical residential conduit depth varies by local code but often ranges from 18-24 inches. However, always check your local codes for specific requirements.
Can I bury conduit deeper than the code minimum?
Yes, burying conduit deeper than the minimum code requirement is generally acceptable and often preferable, particularly in areas with heavy traffic or harsh soil conditions.
What type of backfill is recommended for conduit?
Use compacted, non-corrosive backfill material free of rocks or sharp objects that could damage the conduit. Compacting the soil helps prevent settling and potential damage to the conduit over time.
How do I locate existing utilities before digging?
Contact your local utility companies through a "Call Before You Dig" service (often available online or through a phone number). They will mark the location of underground utilities to prevent accidental damage. This is extremely important and can prevent serious injury or death.
What happens if I damage an underground utility while digging?
Immediately contact the utility company and your local emergency services. Attempting to repair the damage yourself can be extremely dangerous.
By following these steps and understanding the factors that influence conduit depth, you can ensure safe, code-compliant, and long-lasting electrical installations. Always prioritize safety and consult your local building codes for specific requirements in your area. Remember, accurate conduit depth is a critical component of a safe and reliable electrical system.