Bronze or Brass? The Simple Solution
Choosing between bronze and brass can feel overwhelming. Both are beautiful, durable metals with a rich history, often used in similar applications. But understanding their key differences will help you make the right choice for your specific needs. This guide will break down the characteristics of each metal, highlighting their unique properties to guide you towards the perfect material for your project.
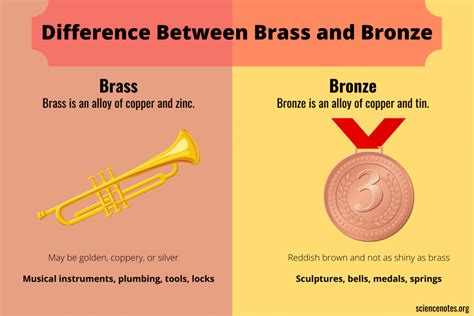
What is Bronze?
Bronze is an alloy primarily composed of copper and tin. The precise ratio of these metals can vary, influencing the final properties of the bronze. This variability allows for a range of bronze types, each with its own distinct characteristics. Generally, bronze is known for its:
- Durability: Bronze is exceptionally resistant to corrosion and weathering, making it ideal for outdoor applications and items requiring longevity.
- Strength: While not as strong as steel, bronze offers significant strength and can be cast into intricate shapes.
- Appearance: Bronze possesses a warm, reddish-brown hue, often developing a beautiful patina over time. This patina is a layer of oxidation that protects the underlying metal from further corrosion and adds to its aesthetic appeal.
What is Brass?
Brass is another alloy, primarily consisting of copper and zinc. Like bronze, the precise ratio of these metals can impact the final properties. Brass is recognized for its:
- Malleability: Brass is relatively easy to work with, allowing for intricate designs and detailed work.
- Appearance: Brass typically exhibits a golden-yellow hue, although this can vary based on the zinc content. It also develops a patina over time, but the color shift is generally less dramatic than with bronze.
- Cost: Brass is generally less expensive than bronze, making it a more budget-friendly option.
Bronze vs. Brass: Key Differences Summarized
| Feature | Bronze | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Alloying Metal | Tin | Zinc |
| Color | Reddish-brown | Golden-yellow |
| Durability/Corrosion Resistance | Extremely High | High, but generally less than bronze |
| Strength | High | Moderate |
| Malleability | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Generally More Expensive | Generally Less Expensive |
| Patina | More pronounced, often dark brown/green | Less pronounced, often a duller yellow |
What are the common uses of Bronze and Brass?
Bronze: Due to its exceptional durability and corrosion resistance, bronze is frequently used in:
- Statues and Sculptures: Many famous historical statues are made of bronze because of its ability to withstand the elements.
- Marine Hardware: Bronze's resistance to saltwater corrosion makes it a crucial material for boat fittings and other marine applications.
- Bearings and Bushings: Bronze is a self-lubricating material, making it suitable for various mechanical applications.
- Musical Instruments: The rich tone of bronze makes it popular for instruments like cymbals and bells.
Brass: Its malleability and relative affordability make brass a common choice for:
- Musical Instruments: Trumpets, trombones, and other brass instruments are frequently made from brass.
- Hardware: Doorknobs, hinges, and other household hardware are often made from brass.
- Plumbing Fittings: Brass is often used in plumbing due to its corrosion resistance.
- Ornamental Items: Brass is used extensively in decorative items due to its attractive golden color and ease of working.
Which Metal is Right for Me?
The best choice depends entirely on your project’s requirements. Consider these factors:
- Budget: Brass is generally less expensive than bronze.
- Durability: If long-term durability and corrosion resistance are paramount, bronze is the better choice.
- Appearance: Consider the desired color and patina development.
- Workability: Brass is easier to work with than bronze.
Ultimately, understanding the distinct characteristics of bronze and brass empowers you to make an informed decision. Weigh the pros and cons of each metal based on your specific needs and aesthetic preferences. Choosing the right metal will ensure your project's success and longevity.
What is the difference in how bronze and brass age?
Both bronze and brass develop a patina over time, a protective layer of oxidation. However, bronze's patina is generally more pronounced and can range from dark brown to green, depending on the environment. Brass's patina is typically a duller yellow or brown, less dramatic in its color change. This difference in patina development contributes to the distinct aesthetic qualities of each metal.
Are bronze and brass toxic?
Bronze and brass themselves are not inherently toxic. However, prolonged exposure to the dust or fumes produced during the manufacturing or machining of these metals can pose health risks. Proper safety precautions, including ventilation and respiratory protection, should always be employed when working with these materials.
Which metal is more sustainable?
The sustainability of both bronze and brass depends largely on the sourcing of the raw materials (copper and tin/zinc) and the manufacturing process. Responsible sourcing and recycling play crucial roles in minimizing the environmental impact of these metals. Both can be recycled, which contributes to their overall sustainability. Choosing materials from reputable sources with a commitment to environmental responsibility is key.